Ascaris lumbricoides
Definition
an intestinal worm
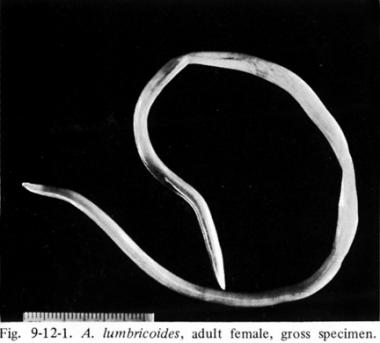
It is a nematode
15 - 35 cm
Incidence :
Affects one fourth to one third of the world's population
Majority asymptomatic
No racial predilection
Male children more due to greater propensity to eat soil.
Children affected more because of ingesting soil
Associated with malnutrition, iron-deficiency anemia and impairments of growth and cognition
Pathophysiology
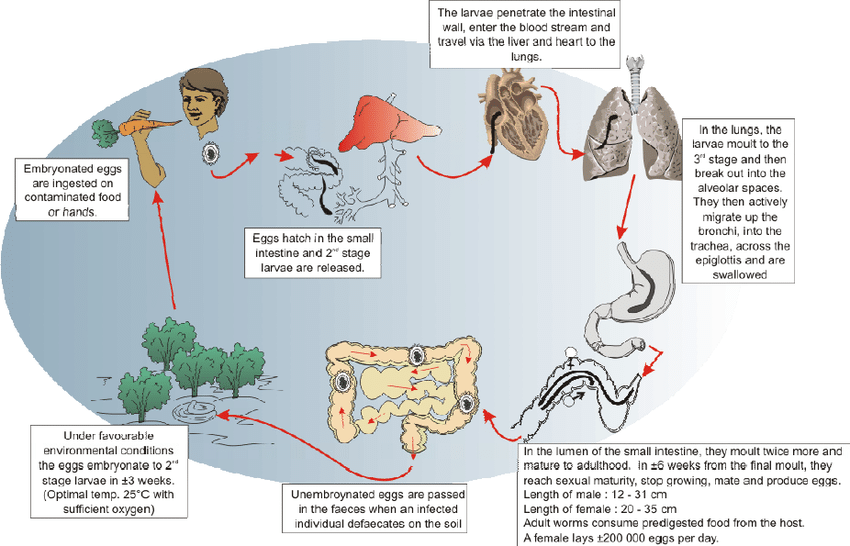
Ingestion of embryonated eggs in feces-contaminated soil or foodstuffs → eggs hatch → live in the small intestine → release small larvae that penetrate the intestinal wall → migrate to pulmonary vascular beds → alveoli via the portal veins - cough wheezing. During this stage no eggs detected in stool of the patient because eggs are not shed in stool until 40 days after the development of pulmonary symptoms. → migrate up in the respiratory tract → swallowed → become matured and lay eggs in the intestines. Adult worms live in the intestine for 8 - 24 months. may cause intestinal obstruction may migrate into the appendix, hepatobiliary system, or pancreatic ducts and rarely other organs such as kidneys or brain
Epidemiology
Worldside
Mortality/Morbidity - intestinal and biliary tract obstruction and its sequelae - 730, 000 cases of bowel obstruction annually of which 11000 of which are fatal.
Prognosis
excellent
Patient education
good personal hygiene and food handling.
hand-washing
avoiding soil consumption
address the use of human feces as fertilizer
Clinical manifestations
2 categories - early (larval migration) and late (mechanical effects)
eosinophilic pneumonia (Loffler syndrome).
fever
Nonproductive cough
Dyspnea
Wheezing
Passage of worms from mouth nares anus
Diffuse or epigastric abdominal pain
Nausea, vomiting
Pharyngeal globus, "tnigling throat"
Frequent throat clearing, dry cough
Small bowel obstruction, volvulus, intussusception, biliary obstruction, appendicitis, pancreatitis
Jaundice (biliary obstruction)
Cachexia (malnutrition)
Pallor (anemia)
Urticaria (early infection)
Wheezing
Rales
Diminished breath sounds
Differential Diagnosis
Acute cholangitis
Acute pancreatitis
Appendicitis
Ascending cholangitis
Asthme
Cholecystitis and biliary colic
Hookworm
Intussusception
Intestinal obstruction
Laboratory Studies
CBC → eosinophilia
Sputum : larvae or Charcot-Leyden crystals (collections of crystalloid composed of eosinophilic proteins)
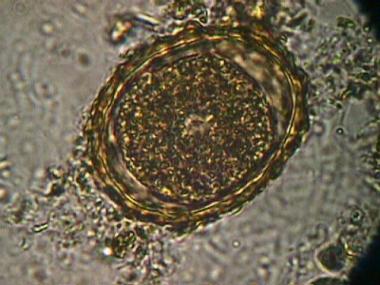
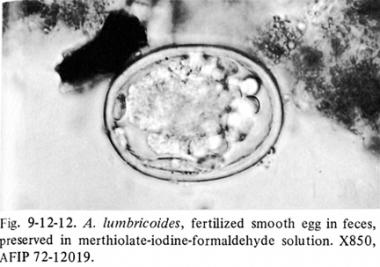
Stool : characteristic eggs 200,000 eggs per day
Ascaris - specific antibodies + not protective
increase in IgE and later IgG
imaging studies : Chest X-ray : patchy infiltrates of eosinophilic pneumonia, intestinal obstruction - air-fluid levels, the "cigar bundle" appearance of a worm bolus